- Article
Leadership Communication Defines Hotel Employees’ Well-Being; Assessment of Socioeconomic Status and Trust in Leader
- Pouya Zargar and
- Panteha Farmanesh
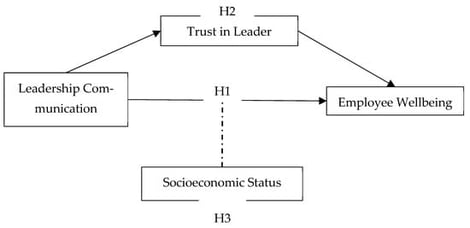
Leadership is a key predictor of employees’ well-being, especially in sectors with high labor intensity and role changes, such as the hotel sector. Leadership communication can act as a major job resource element in forming positive exchanges with employees. This research investigates the influence of leadership communication on employees’ well-being in luxury hotels across five Middle Eastern countries, namely Jordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Bahrain. Combining social exchange theory and the job demand-resources model, the indirect effects of trust in leader as a mediator and moderating influence of socioeconomic status are examined. Using a quantitative and deductive approach and a cross-sectional survey, a total of 380 employee data was collected and analyzed using a partial least squares–structural equation modeling technique in Smart-PLS software. (version 4). The dimensions of leadership communication had a significant link with the well-being of hotel staff. While the mediating influence of trust in leader was found to be partially significant, the inclusion of socioeconomic status as a moderator complements the findings. The results suggest that while appropriate leadership communication is essential and can establish trust, the socioeconomic status of employees in the high-demand, low-resource hotel sector is a crucial matter. The findings can be beneficial for scholars looking into regional and sectoral assessment as well as practitioners seeking to improve employees’ well-being in the Middle Eastern hotel sector.
10 February 2026